Introduction
The Poseidon Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM) played a crucial role in the U.S.’s nuclear strategy during the Cold War. It signified the U.S.’s choice to place most of its nuclear warheads in its sea-based deterrent force. This decision was part of the Triad deterrent strategy.
Deployment
In 1971, the deployment of the Poseidon C3 SLBM began. It coincided with the phase-out of the Polaris A2 SLBM in 1974 and the Polaris A3 in 1982.
The U.S. Navy converted thirty-one nuclear ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs) of the Lafayette, Madison, and Benjamin Franklin classes to carry the new missile. The following table displays the conversion dates:
| SSBN | Conversion Yard | Start | Complete |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lafayette (SSBN-616) | Electric Boat | 15 Oct 1972 | 7 Nov 1974 |
| Alexander Hamilton (SSBN-617) | Newport News | 15 Jan 1973 | 11 Apr 1975 |
| Andrew Jackson (SSBN-619) | Electric Boat | 19 Mar 1973 | 15 Aug 1975 |
| John Adams (SSBN-620) | Portsmouth NSYd | 1 Feb 1974 | 15 Apr 1976 |
| James Monroe (SSBN-622) | Newport News | 15 Jan 1975 | 14 May 1977 |
| Nathan Hale (SSBN-623) | Puget Sound NSYd | 15 June 1973 | 27 June 1975 |
| Woodrow Wilson (SSBN-624) | Newport News | 1 Oct 1973 | 23 Oct 1975 |
| Henry Clay (SSBN-625) | Portsmouth NSYd | 29 Apr 1975 | 29 July 1977 |
| Daniel Webster (SSBN-626) | Electric Boat | 1 Dec 1975 | 21 Feb 1978 |
| James Madison (SSBN-627) | Electric Boat | 3 Feb 1969 | 28 June 1970 |
| Tecumseh (SSBN-628) | Newport News | 10 Nov 1969 | 18 Feb 1971 |
| Daniel Boone (SSBN-629) | Newport News | 11 May 1969 | 11 Aug 1970 |
| John C. Calhoun (SSBN-630) | Mare I NSYd | 4 Aug 1969 | 22 Feb 1971 |
| Ulysses S. Grant (SSBN-631) | Puget Sound NSYd | 3 Oct 1969 | 16 Dec 1970 |
| Von Steuben (SSBN-632) | Electric Boat | 11 July 1969 | 19 Nov 1970 |
| Casimir Pulaski SSBN-633) | Electric Boat | 10 Jan 1970 | 30 Apr 1971 |
| Stonewall Jackson (SSBN-634 | Electric Boat | 15 July 1970 | 29 Oct 1971 |
| Sam Rayburn (SSBN-635) | Portsmouth NSYd | 19 Jan 1970 | 2 Sep 1971 |
| Nathanael Greene (SSBN-636) | Newport News | 22 July 1970 | 21 Sep 1971 |
| Benjamin Franklin (SSBN-640) | Electric Boat | 25 Feb 1971 | 15 May 1972 |
| Simon Bolivar (SSBN-641) | Newport News | 15 Feb 1971 | 12 May 1972 |
| Kamehameha (SSBN-642) | Electric Boat | 15 July 1971 | 27 Oct 1972 |
| George Bancroft (SSBN-643) | Portsmouth NSYd | 28 Apr 1971 | 31 July 1972 |
| Lewis and Clark (SSBN-644) | Puget Sound NSYd | 30 Apr 1971 | 21 July 1972 |
| James K. Polk (SSBN-645) | Newport News | 15 July 1971 | 17 Nov 1972 |
| George C. Marshall (SSBN-654) | Puget Sound NSYd | 14 Sep 1971 | 8 Feb 1973 |
| Henry L. Stimson (SSBN-655) | Newport News | 15 Nov 1971 | 22 Mar 1973 |
| George Washington (SSBN-Carver 656) | Electric Boat | 12 Nov 1971 | 7 Apr 1973 |
| Francis Scott Key (SSBN-657) | Puget Sound NSYd | 20 Feb 1972 | 17 May 1973 |
| Mariano G. Vallejo (SSBN-658) | Newport News | 21 Aug 1972 | 19 Dec 1973 |
| Will Rogers (SSBN-659) | Portsmouth NSYd | 16 Oct 1972 | 8 Feb 1974 |
By 1978, the U.S. had thirty-one Lafayette-class SSBNs with Poseidon C-3 missiles. These submarines carried 496 Poseidon C3 missiles. These missiles contained 4,960 W68 thermonuclear warheads. Each warhead within its own Mk 3 RV.
This was a significant increase. The Poseidon’s peak deployment had 4,960 warheads. In contrast, the Polaris had a peak of only 656 warheads. This means the Poseidon had over 650% more warheads than the Polaris.
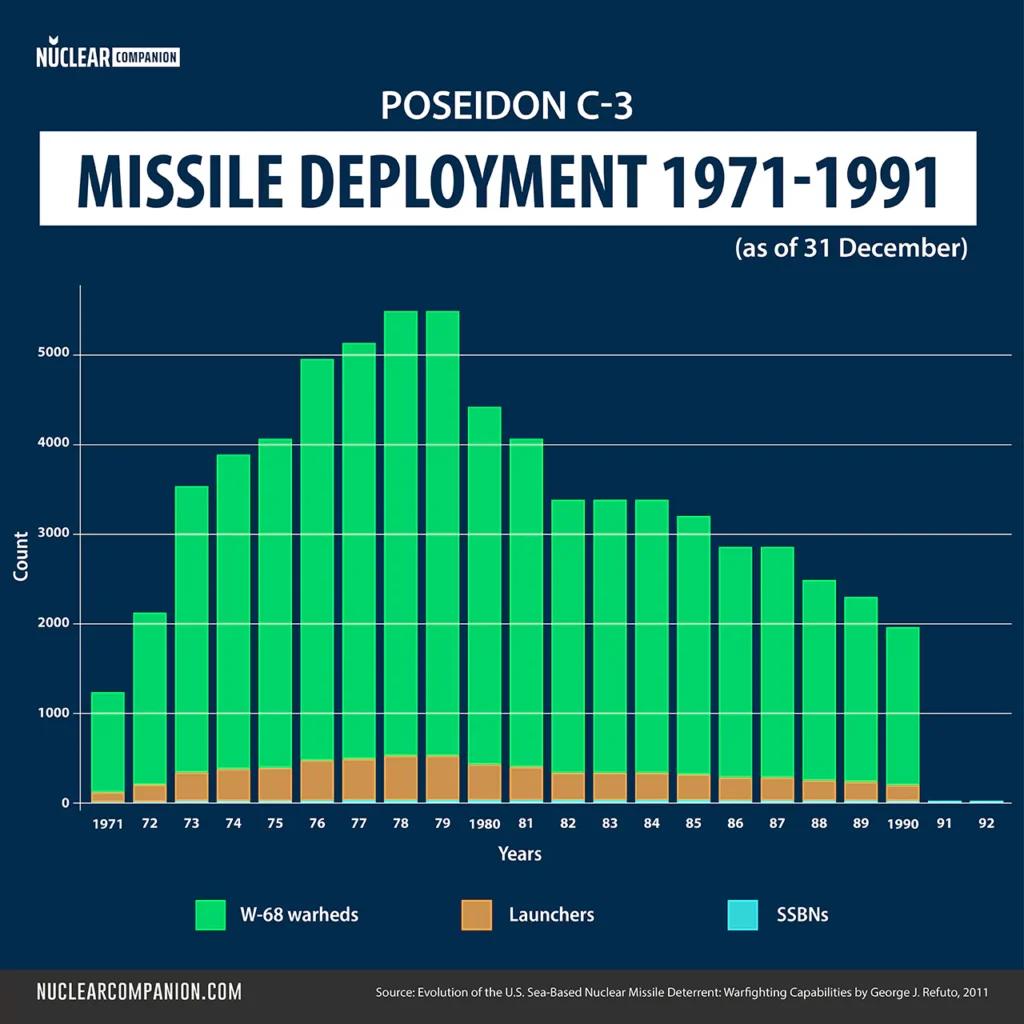
However, by 1991, the Poseidon C3 SLBM was phased out. This phase-out happened alongside the start of the Trident I C4 SLBM deployment in 1979. Then, in 1990, the Trident II D5 SLBM was deployed. This was around the time the last Poseidon SLBM was retired. Two years after the Poseidon was phased out, the last Lafayette-class SSBN was also withdrawn. Its Trident I C4 missiles moved to the Ohio-class SSBNs.
SSBNs, SLBM Launchers & Warheads
The table below details the Poseidon C3 deployment from 1971 to 1991 (as of December 31):
| Year | SSBNs | Launchers | W-68 Warheds |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1971 | 7 | 112 | 1120 |
| 1972 | 12 | 192 | 1920 |
| 1973 | 20 | 320 | 3200 |
| 1974 | 22 | 352 | 3520 |
| 1975 | 23 | 368 | 3680 |
| 1976 | 28 | 448 | 4480 |
| 1977 | 29 | 464 | 4640 |
| 1978 | 31 | 496 | 4960 |
| 1979 | 31 | 496 | 4960 |
| 1980 | 31 | 400 | 4000 |
| 1981 | 31 | 368 | 3680 |
| 1982 | 31 | 304 | 3040 |
| 1983 | 31 | 304 | 3040 |
| 1984 | 31 | 304 | 3040 |
| 1985 | 30 | 288 | 2880 |
| 1986 | 28 | 256 | 2560 |
| 1987 | 28 | 256 | 2560 |
| 1988 | 26 | 224 | 2240 |
| 1989 | 25 | 208 | 2080 |
| 1990 | 23 | 176 | 1760 |
| 1991 | 12 | 0 | 0 |
| 1992 | 11 | 0 | 0 |
| 1993 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Further reading
- United States Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBM)
- Polaris A-2 (UGM-27B)
- Polaris A-3 (UGM-27C)
- Trident I C-4 (UGM-96)
- Trident I C-4 Missile Deployment (1979-2004)
- Trident II D-5 (UGM-133A)
Bibliography
- Evolution of the U.S. Sea-Based Nuclear Missile Deterrent: Warfighting Capabilities by George J. Refuto, 2011