Introduction
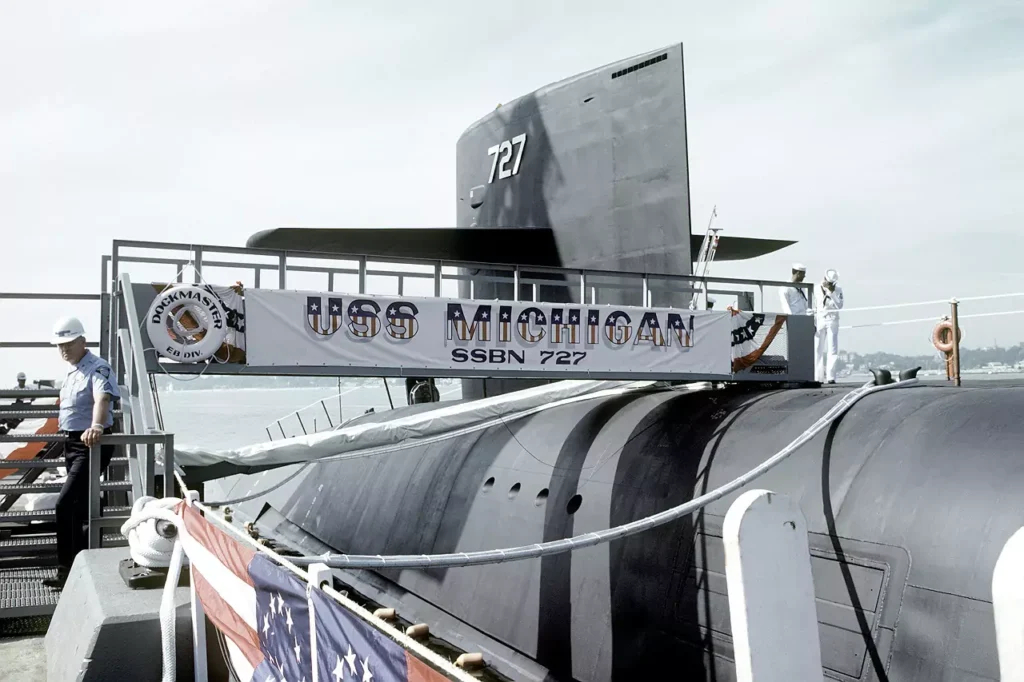
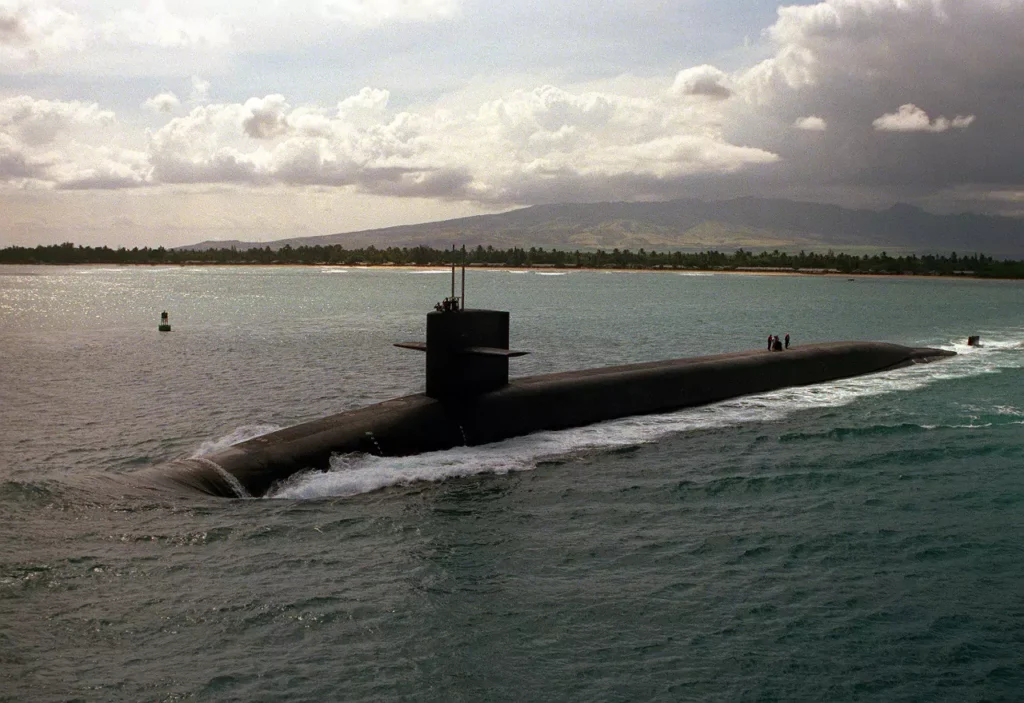
USS MICHIGAN (SSBN 727) is the second Trident Class Nuclear Powered Fleet Ballistic Missile Submarine built by the Electric Boat Division of General Dynamics Corporation in Groton, Connecticut. She was equipped to carry 24 Trident I C-4 missiles.
Her keel was laid on 4 April 1977, and she was commissioned on 11 September 1982. As the third United States Navy vessel to bear the name of the state of Michigan, the USS MICHIGAN arrived at Bangor, Washington, on 16 March 1983.
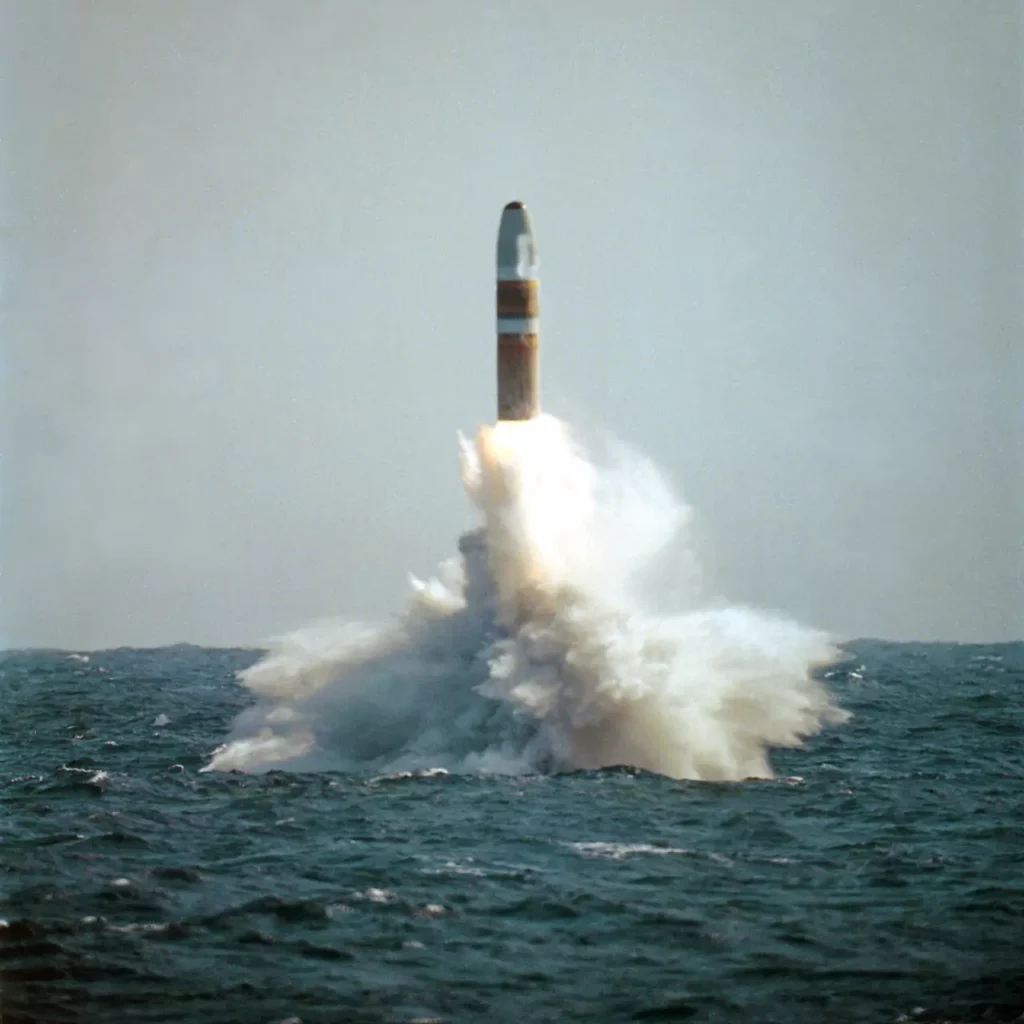

During her service, she completed 67 Strategic Deterrent Patrols.
In 2004, USS MICHIGAN (SSBN 727) was officially redesignated as a Guided Missile Submarine (SSGN 727). This marked the beginning of her conversion to support cruise missiles and special forces missions.
Note: This article covers only her history as a ballistic submarine.
Namesake
USS MICHIGAN is the third United States Navy vessel to be named after the state of Michigan.
The first USS MICHIGAN (1843-1922) was the first iron warship in the U.S. Navy.
The second USS MICHIGAN (BB-27) was a battleship built by the New York Shipbuilding Company. Laid down on 17 December 1906, launched on 26 May 1908, and commissioned on 4 January 1910, she served until her decommissioning on 11 February 1922 at the Philadelphia Navy Yard.
Specifications
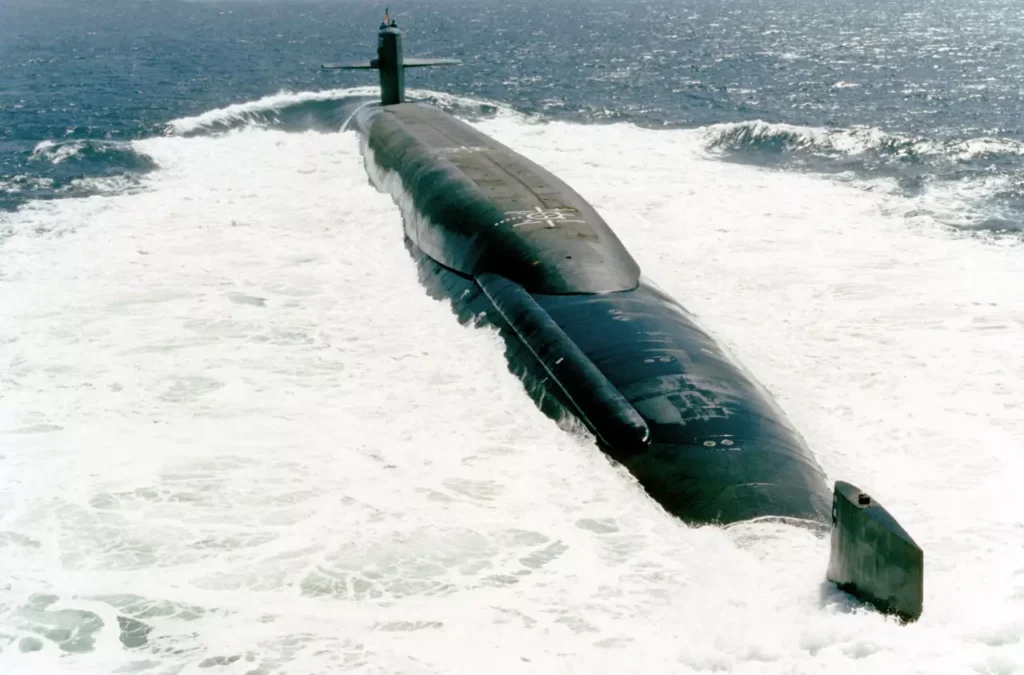
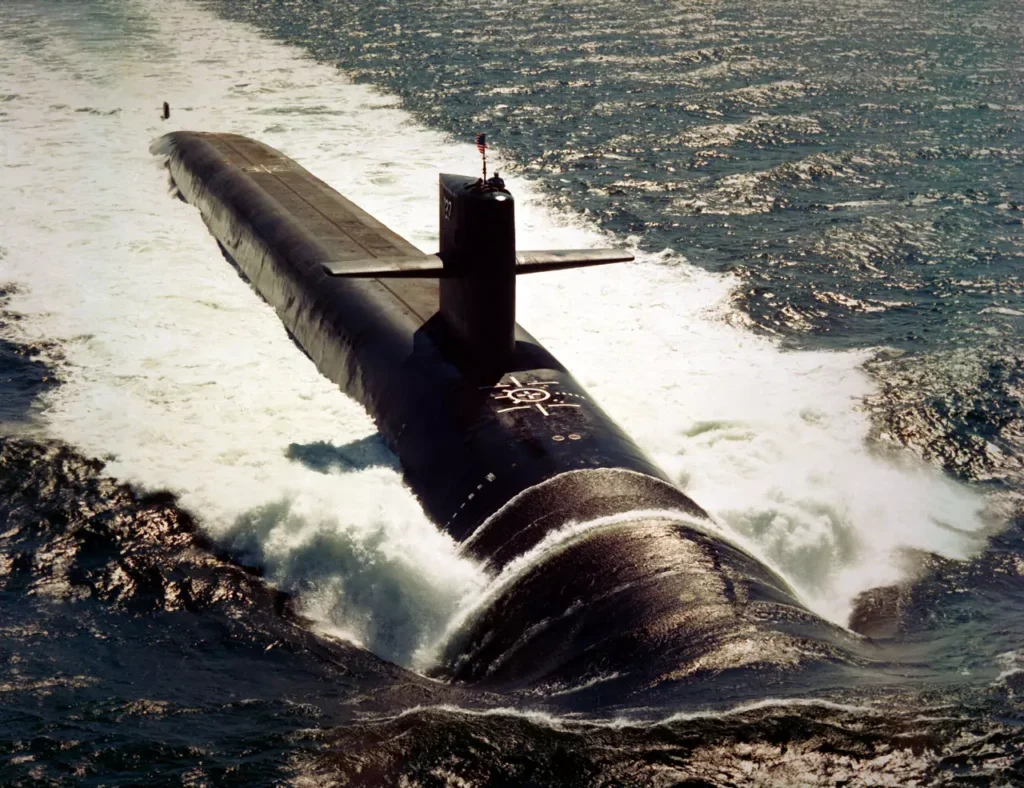
The Trident SSBN is the largest submarine built in the United States. It is 560 feet long, has a diameter of 42 feet, and displaces 18,700 tons when submerged. These submarines are as large as buildings. This is because they have a big nuclear reactor and are designed to carry Trident II missiles. These missiles are thirty-four feet high and stored vertically inside the submarine.
Check Ohio-Class (SSBN-726) Submarine Technical Specification for the ship’s detailed characteristics.
Construction
- Builder: General Dynamics Electric Boat Division
- Fund Approval:
- Contract awarded:
- Keel laying ceremony: 4 APRIL 1977
- Keel laid’s Sponsor: Mrs. Margaret Garvey Nedzi, wife of Congressman Lucien N. Nedzi
- Launched: 26 APRIL 1980
- Christen by: Mrs. Margaret Garvey Nedzi, wife of Congressman Lucien N. Nedzi
- Sea trials start: 21 MAY 1982
- Delivered: 28 AUGUST 1982
Commissioning
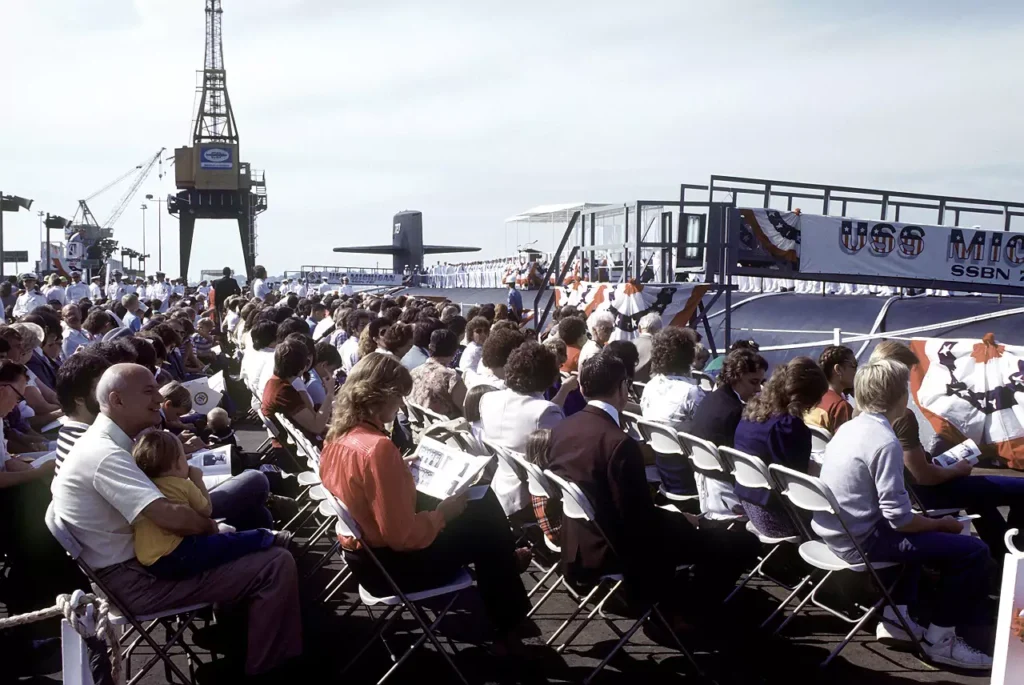

- Commissioned: 11 September 1982
- Principal speaker: ADM Kinnaird R. McKee, Director of the Division of Naval Reactors
- Commanding Officer Blue Crew: Captain W. E. Rickman
- Commanding Officer Gold Crew: Captain F. M. Conway III
Service
- 21 November 1982 – The Blue Crew of USS MICHIGAN (SSBN 727) successfully launched its first TRIDENT I (C4) missile in support of the ship’s Demonstration and Shakedown Operation.
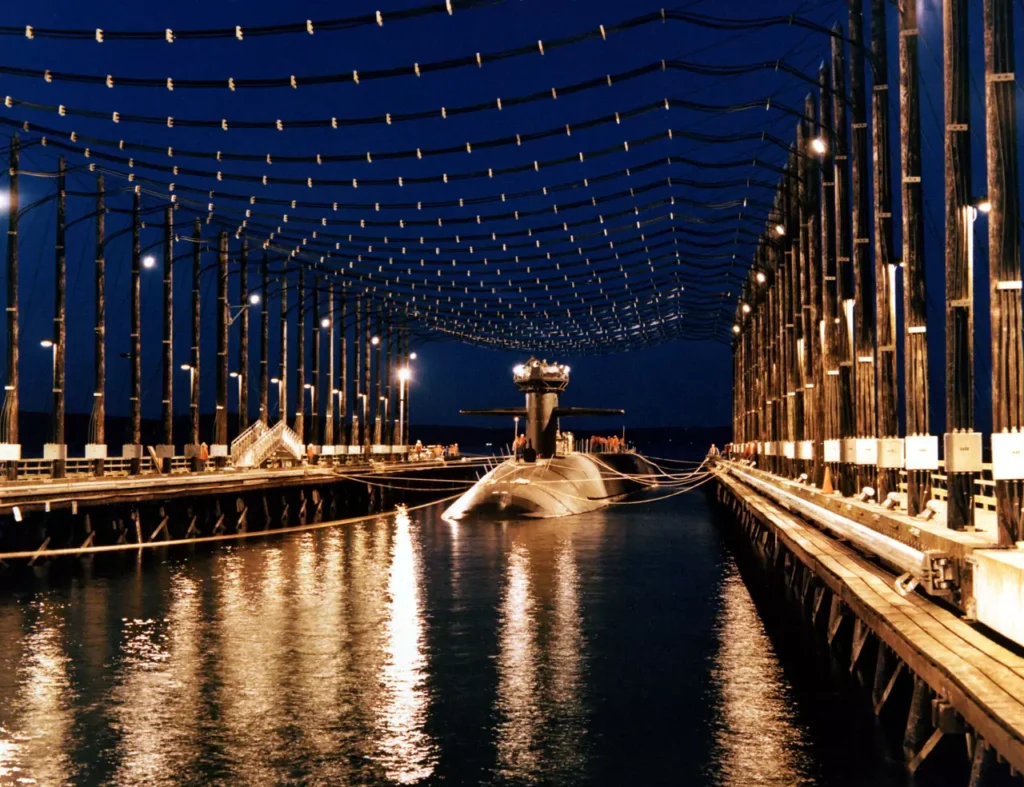
- 16 March 1983 – The arrival of USS MICHIGAN (SSBN 727) at Bangor, WA
- 3 June 1983 – Completed her first strategic loadout at Strategic Weapons Facility, Pacific, Bremerton, WA.
- 1 October 2003 – She was removed from strategic service before conversion to SSGN.
- 1 January 2004 – USS MICHIGAN (SSBN 727) entered Puget Sound Naval Shipyard for SSGN Conversion.
Assignments
| Dates | Unit | Location |
|---|---|---|
| March 1983 - January 2004 | Submarine Squadron (SUBRON ) 17 | Bangor, Wash |
Overhauls & Conversions
| Location | Start | End | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Puget Sound Naval Shipyard | 1 October 1994 | 7 June 1995 | Second Trident Engineered overhaul (EOH) |
| Puget Sound Naval Shipyard | 1 January 2004 | 22 November 2006 | SSGN Conversion |
Missile Launches
- DASO (Demonstration and Shakedown Operation). These were launches conducted to demonstrate the readiness of the Trident Weapon System and its crew for deployment.
- CINC – Commander-in-Chief.
- OT (Operational Test) / CET (CINC Evaluation Test) These tests provided initial data on the reliability and accuracy of the missile.
- FOT (Follow-on Operational Test / FCET (Follow-On CINC Evaluation Test). Annual launches were designed to ensure that the reliability and accuracy factors were preserved during the system’s life and carried out under tactical conditions to exercise all weapon system elements.
The table below details the launches from 1982 to 2001:
| # | Date | Type | Missile | Status | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21 November 1982 | DASO | Trident C4 | Successfull | Blue Crew |
| 2 | 2 July 1984 | OT | Trident C4 | Successfull | |
| 3 | 2 July 1984 | OT | Trident C4 | Successfull | |
| 4 | 2 July 1984 | OT | Trident C4 | Successfull | |
| 5 | 2 July 1984 | OT | Trident C4 | Successfull | |
| 6 | 22 April 1985 | FOT | Trident C4 | Successfull | |
| 7 | 22 April 1985 | FOT | Trident C4 | Successfull | |
| 8 | 22 April 1985 | FOT | Trident C4 | Successfull | |
| 9 | 22 April 1985 | FOT | Trident C4 | Successfull | |
| 10 | 12 September 1986 | FOT | Trident C4 | Successfull | |
| 11 | 12 September 1986 | FOT | Trident C4 | Successfull | |
| 12 | 29 JULY 1993 | FOT | Trident C4 | Successfull | Gold Crew |
| 13 | 29 JULY 1993 | FOT | Trident C4 | Successfull | Gold Crew |
| 14 | 29 JULY 1993 | FOT | Trident C4 | Successfull | Gold Crew |
| 15 | 29 JULY 1993 | FOT | Trident C4 | Successfull | Gold Crew |
| 16 | 29 October 1995 | DASO | Trident C4 | Successfull | Gold Crew. DASO following EOH. |
Photo Gallery






Further reading
- United States Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBM)
- Ohio-Class (SSBN-726) Ballistic Missile Submarines
- Ohio-Class (SSBN-726) Submarine Technical Specification
Other ships of the class:
Bibliography
- Facts/Chronology: Polaris, Poseidon, Trident, 50th Anniversary, Strategic Systems Programs, 2005
- Polmar, N. (2013). The Naval Institute Guide to the Ships and Aircraft of the U.S. Fleet. United Kingdom: Naval Institute.